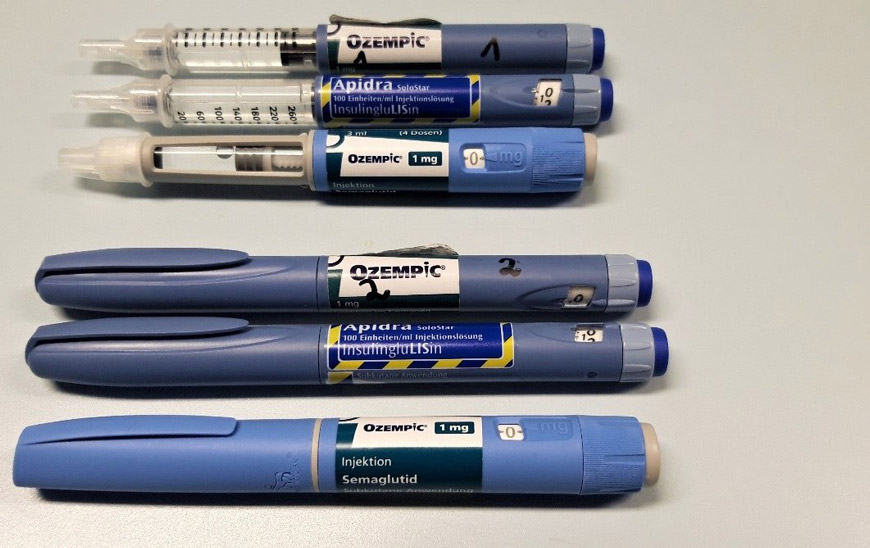
Following concerns that falsified batches of Ozempic® may have entered the market, the Official Medicines Control Laboratory (OMCL) Chemisches und Veterinäruntersuchungsamt (CVUA, Karlsruhe, Germany) and a member of the European OMCL Network, has determined by analytical testing that suspected batches of Ozempic® pre-filled pens contained insulin glulisine instead of the claimed active substance, semaglutide. More information on this discovery can be found in a scientific paper published by CVUA on 22 November 2023 (in German).
Ozempic® is a medicinal product authorised to treat type 2 diabetes, but it has also become an extremely popular weight-loss treatment due to its appetite suppressant properties and ability to trigger insulin production. This off-label use for weight-loss has led to shortages in the legal supply chain, making it a prime target for falsification. Since October 2023, authorities from several countries have issued warnings concerning dangerous falsified versions of Ozempic® pens, which if used could have life-threatening consequences, including hypoglycaemic shock and coma.
See also:
- Ozempic® - the diabetes injection that is also used as a "slimming product". Suspected falsification now also confirmed analytically (English translation).
Image copyright: CVUA Karlsruhe